Brian McCullough, host of the Internet History Podcast, does an excellent job of showing how the individuals adopted the internet and made it central to their lives. He follows not only the success stories but also the flame outs which provide an accurate history of a time of rapid technological change.
Tech Themes
Form to Factor: Design in Mobile Devices. Apple has a long history with mobile computing, but a few hiccups in the early days are rarely addressed. These hiccups also telegraph something interesting about the technology industry as a whole - design and ease of use often trump features. In the early 90’s Apple created the Figaro, a tablet computer that weighed eight pounds and allowed for navigation through a stylus. The issue was it cost $8,000 to produce and was 3/4 of an inch thick, making it difficult to carry. In 1993, the Company launched the Newton MessagePad, which cost $699 and included a calendar, address book, to-do list and note pad. However, the form was incorrect again; the MessagePad was 7.24 in. x 4.5 in. and clunky. With this failure, Apple turned its attention away from mobile, allowing other players like RIM and Blackberry to gain leading market share. Blackberry pioneered the idea of a full keyboard on a small device and Marc Benioff, CEO of salesforce.com, even called it, “the heroin of mobile computing. I am serious. I had to stop.” IBM also tried its hand in mobile in 1992, creating the Simon Personal Communicator, which had the ability to send and receive calls, do email and fax, and sync with work files via an adapter. The issue was the design - 8 in. by 2.5 in. by 1.5 in. thick. It was a modern smartphone, but it was too big, clunky, and difficult to use. It wasn’t until the iPhone and then Android that someone really nailed the full smart phone experience. The lessons from this case study offer a unique insight into the future of VR. The company able to offer the correct form factor, at a reasonable price can gain market share quickly. Others who try to pioneer too much at a time (cough, magic leap), will struggle.
How to know you’re onto something. Facebook didn’t know. On November 30, 2004, Facebook surpassed one million users after being live for only ten months. This incredible growth was truly remarkable, but Mark Zuckerberg still didn’t know facebook was a special company. Sean Parker, the founder of Napster, had been mentoring Zuckerberg the prior summer: “What was so bizarre about the way Facebook was unfolding at that point, is that Mark just didn’t totally believe in it and wanted to go and do all these other things.” Zuckerberg even showed up to a meeting at Sequoia Capital still dressed in his pajamas with a powerpoint entitled: “The Top Ten Reasons You Should Not Invest.” While this was partially a joke because Sequoia has spurned investing in Parker’s latest company, it represented how immature the whole facebook operation was, in the face of rapid growth. Facebook went on to release key features like groups, photos, and friending, but most importantly, they developed their revenue model: advertising. The quick user growth and increasing ad revenue growth got the attention of big corporations - Viacom offered $2B in cash and stock, and Yahoo offered $1B all cash. By this time, Zuckerberg realized what he had, and famously spurned several offers from Yahoo, even after users reacted negatively to the most important feature that facebook would ever release, the News Feed. In today’s world, we often see entrepreneur’s overhyping their companies, which is why Silicon Valley was in-love with dropout founders for a time, their naivite and creativity could be harnessed to create something huge in a short amount of time.
Channel Partnerships: Why apple was reluctant to launch a phone. Channel partnerships often go un-discussed at startups, but they can be incredibly useful in growing distribution. Some industries, such as the Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) market thrives on channel partnership arrangements. Companies like Crowdstrike engage partners (mostly IT services firms) to sell on their behalf, lowering Crowdstrike’s customer acquisition and sales spend. This can lead to attractive unit economics, but on the flip side, partners must get paid and educated on the selling motion which takes time and money. Other channel relationships are just overly complex. In the mid 2000’s, mobile computing was a complicated industry, and companies hated dealing with old, legacy carriers and simple clunky handset providers. Apple tried the approach of working with a handset provider, Motorola, but they produced the terrible ROKR which barely worked. The ROKR was built to run on the struggling Cingular (would become AT&T) network, who was eager to do a deal with Apple in hopes of boosting usage on their network. After the failure of the ROKR, Cingular executives begged Jobs to build a phone for the network. Normally, the carriers had specifications for how phones were built for their networks, but Jobs ironed out a contract which exchanged network exclusivity for complete design control, thus Apple entered into mobile phones. The most important computing device of the 2000’s and 2010’s was built on a channel relationship.
Business Themes
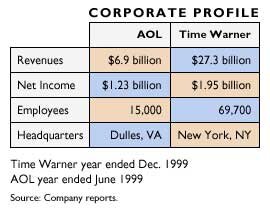
AOL-Time Warner: the merger destined to fail. To fully understand the AOL-Time Warner merger, you must first understand what AOL was, what it was becoming, and why it was operating on borrowed time. AOL started as an ISP, charging customers $9.95 for five hours of dial-up internet access, with each additional hour costing $2.95. McCullough describes AOL: “AOL has often been described as training wheels for the Internet. For millions of Americans, their aol.com address was their first experience with email, and thus their first introduction to the myriad ways that networked computing could change their lives.” AOL grew through one of the first viral marketing campaigns ever; AOL put CDs into newspapers which allowed users to download AOL software and get online. The Company went public in March of 1992 and by 1996 the Company had 2.1 million subscribers, however subscribers were starting to flee to cheaper internet access. It turned out that building an ISP was relatively cheap, and the high margin cash flow business that AOL had built was suddenly threatened by a number of competitors. AOL persisted with its viral marketing strategy, and luckily many americans still had not tried the internet yet and defaulted to AOL as being the most popular. AOL continued to add subscribers and its stock price started to balloon; in 1998 alone the stock went up 593%. AOL was also inking ridiculous, heavily VC funded deals with new internet startups. Newly public Drkoop, which raised $85M in an IPO, signed a four year $89M deal to be AOL’s default provider of health content. Barnes and Noble paid $40M to be AOL’s bookselling partner. Tel-save, a long distance phone provider signed a deal worth $100M. As the internet bubble continued to grow, AOL’s CEO, Steve Case realized that many of these new startups would be unable to fufill their contractual obligations. Early web traffic reporting systems could easily be gamed, and companies frequently had no business model other than attract a certain demographic of traffic. By 1999, AOL had a market cap of $149.8B and was added to the S&P 500 index; it was bigger than both Disney and IBM. At this time, the world was shifting away from dial-up internet to modern broadband connections provided by cable companies. One AOL executive lamented: “We all knew we were living on borrowed time and had to buy something of substance by using that huge currency [AOL’s stock].” Time Warner was a massive media company, with movie studios, TV channels, magazines and online properties. On Jan 10, 2000, AOL merged with Time Warner in one of the biggest mergers in history. AOL owned 56% of the combined company. Four days later, the Dow peaked and began a downturn which would decimate hundreds of internet businesses built on foggy fundamentals. Acquisitions happen for a number of reasons, but imminent death is not normally considered by analysts or pundits. When you see acquisitions, read the press release and understand why (at least from a marketing perspective), the two companies made a deal. Was the price just astronomical (i.e. Instagram) or was their something very strategic (i.e. Microsoft-Github)? When you read the press release years later, it should indicate whether the combination actually was proved out by the market.
Acquisitions in the internet bubble: why acquisitions are really just guessing. AOL-Time Warner shows the interesting conundrum in acquisitions. HP founder David Packard coined this idea somewhat in Packard’s law: “No company can consistently grow revenues faster than its ability to get enough of the right people to implement that growth and still become a great company. If a company consistently grows revenue faster than its ability to get enough of the right people to implement that growth, it will not simply stagnate; it will fall.” Author of Good to Great, Jim Collins, clarified this idea: “Great companies are more likely to die of ingestion of too much opportunity, than starvation from too little.” Acquisitions can be a significant cause of this outpacing of growth. Look no further than Yahoo, who acquired twelve companies between September 1997 and June 1999 including Mark Cuban’s Broadcast.com for $5.7B (Kara Swisher at WSJ in 1999), GeoCities for $3.6B, and Y Combinator founder Paul Graham’s Viaweb for $48M. They spent billions in stock and cash to acquire these companies! Its only fitting that two internet darlings would eventually end up in the hands of big-telecom Verizon, who would acquire AOL for $4.4B in 2015, and Yahoo for $4.5B in 2017, only to write down the combined value by $4.6B in 2018. In 2013, Yahoo would acquire Tumblr for $1.1B, only to sell it off this past year for $3M. Acquisitions can really be overwhelming for companies, and frequently they don’t work out as planned. In essence, acquisitions are guesses about future value to customers and rarely are they as clean and smart as technology executives make them seem. Some large organizations have gotten good at acquisitions - Google, Microsoft, Cisco, and Salesforce have all made meaningful acquisitions (Android, Github, AppDynamics, ExactTarget, respectively).
Google and Excite: the acquisition that never happened. McCullough has an incredible quote nestled into the start of chapter six: “Pioneers of new technologies are rarely the ones who survive long enough to dominate their categories; often it is the copycat or follow-on names that are still with us to this day: Google, not AltaVista, in search; Facebook, not Friendster, in social networks.” Amazon obviously bucked this trend (he mentions that), but in search he is absolutely right! In 1996, several internet search companies went public including Excite, Lycos, Infoseek, and Yahoo. As the internet bubble grew bigger, Yahoo was the darling of the day, and by 1998, it had amassed a $100B market cap. There were tons of companies in the market including the players mentioned above and AltaVista, AskJeeves, MSN, and others. The world did not need another search engine. However, in 1998, Google founders Larry Page and Sergey Brin found a better way to do search (the PageRank algorithm) and published their famous paper: “The Anatomy of a Large-Scale Hypertextual Web Search Engine.” They then went out to these massive search engines and tried to license their technology, but no one was interested. Imagine passing on Goolge’s search engine technology. In an over-ingestion of too much opportunity, all of the search engines were trying to be like AOL and become a portal to the internet, providing various services from their homepages. From an interview in 1998, “More than a "portal" (the term analysts employ to describe Yahoo! and its rivals, which are most users' gateway to the rest of the Internet), Yahoo! is looking increasingly like an online service--like America Online (AOL) or even CompuServe before the Web.” Small companies trying to do too much (cough, uber self-driving cars, cough). Excite showed the most interest in Google’s technology and Page offered it to the Company for $1.6M in cash and stock but Excite countered at $750,000. Excite had honest interest in the technology and a deal was still on the table until it became clear that Larry wanted Excite to rip out its search technology and use Google’s instead. Unfortunately that was too big of a risk for the mature Excite company. The two companies parted ways and Google eventually became the dominant player in the industry. Google’s focus was clear from the get-go, build a great search engine. Only when it was big enough did it plunge into acquisitions and development of adjacent technologies.
Dig Deeper
Raymond Smith, former CEO of Bell Atlantic, describing the technology behind the internet in 1994
Bill Gates’ famous memo: THE INTERNET TIDAL WAVE (May 26, 1995)
List of all the companies made famous and infamous in the dot-com bubble
Pets.com S-1 (filing for IPO) showin a $62M net loss on $6M in revenue